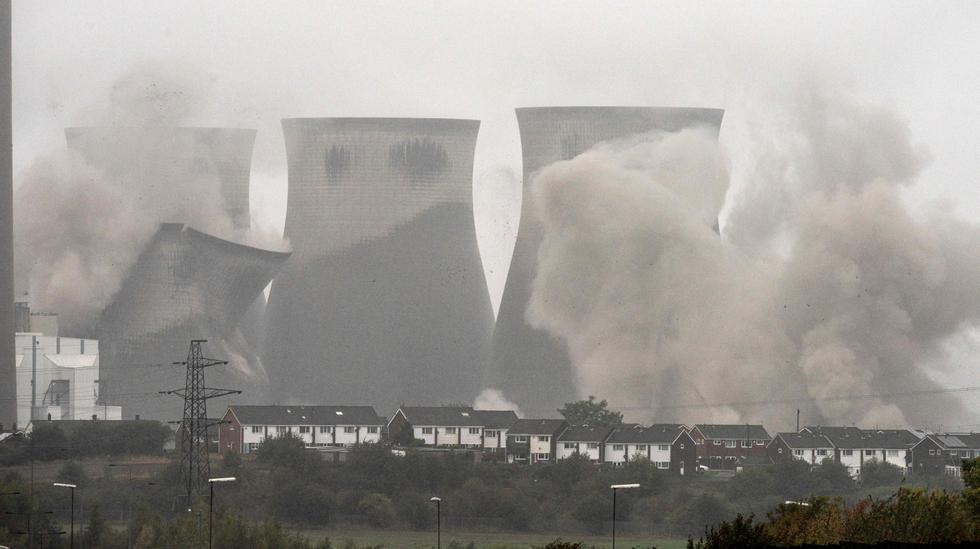
Early this morning, Tuesday 28 April, the UK set a new record when the country did not burn coal to generate electricity for 18 days, six hours and 15 minutes, writes the climate website Carbon Summary.
One of the reasons for this new record is the coronavirus which has cut electricity demand in the country by 20 percent.
Over the 18-day period, renewable energy accounted for 37 percent of electricity supply, gas 32 percent, nuclear power 22 percent, and 9 percent of electricity imported from France, Belgium, and the Netherlands.
There will be a major shift from coal and other fossil fuels to renewable energy in the UK. The country aims to phase out coal use by 2024, and this is ahead of schedule.
Also read: Producing countries are inflating climate budgets
From more than 40 percent coal to close to zero
Carbon Summary summarizes historical developments:
Article continues below advertisementArticle continues below advertisement
- In 2012, coal accounted for 43 percent of all electricity supply in the UK. In 2015, the proportion of coal fell to 25 percent. In 2019, coal’s share fell to 2 percent.
- On 9 May 2016, the UK electricity grid operated without coal for the first time since it was founded in 1882. This lasted for four hours. In April 2017, the power grid operated without coal for a full day for the first time. The first coal-free week occurred last May. The previous coal-free record of 18 days, six hours and ten minutes occurred not long after.
- Fossil energy accounted for 69 percent of all electricity supply in 2012. So far in 2020, fossil energy accounts for 36 percent of electricity supply.
- The proportion of renewable energy has increased from 7 percent in 2012 to 38 percent in 2020. Wind energy is the largest contributor.
Coal is a form of energy that produces the highest CO2 – emissions from the forms of energy we use to generate electricity, according to an overview of UN climate panel.
Coal is also on the decline in the US
The amount of coal used in electricity supply is also decreasing in America. At the same time, the amount of renewable energy is increasing.
In the first two months of 2020, coal consumption fell by 33 percent compared to the first two months of 2019. This can be seen from the figures from the US Energy Agency. AMDAL.
Also read: Trump’s coal dreams are crumbling
In the same period, the amount of electricity generated from wind energy increased by 19 percent, and now accounts for nearly 9 percent of the total electricity supply in the United States.
The amount of electricity from solar energy increased by 32 percent in the first two months of 2020 compared to 2019. Solar energy now accounts for about two percent of the total electricity supply in the United States.

“Social media guru. Total beer fanatic. Tv ninja. Typical coffee fan. Amateur entrepreneur. Unapologetic food scholar.”